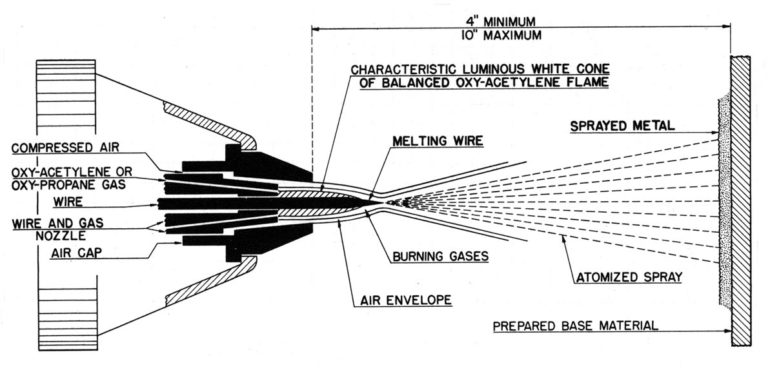
The material, in wire form, is melted in a flame (usually oxy—acetylene flame). The molten particles are propelled to the substrate with compressed air. Flame temperature is lower compared to the other spraying techniques (about 2000 — 2500°C) and so is the particle velocity during spraying. It is a relatively easy to use method, simple in operation and with high deposition rates, that can be used in wear and corrosion applications.
Common materials, sprayed with this method, include:
- Zn
- Al
- Mo
- NiCr
- Steels
